| .. | ||
| RELEASE.2023-05-04T21-44-30Z | ||
| data.yml | ||
| logo.png | ||
| README.md | ||
MinIO Quickstart Guide
MinIO is a High Performance Object Storage released under GNU Affero General Public License v3.0. It is API compatible with Amazon S3 cloud storage service. Use MinIO to build high performance infrastructure for machine learning, analytics and application data workloads.
This README provides quickstart instructions on running MinIO on bare metal hardware, including container-based installations. For Kubernetes environments, use the MinIO Kubernetes Operator.
Deployment Recommendations
Allow port access for Firewalls
By default MinIO uses the port 9000 to listen for incoming connections. If your platform blocks the port by default, you may need to enable access to the port.
ufw
For hosts with ufw enabled (Debian based distros), you can use ufw command to allow traffic to specific ports. Use below command to allow access to port 9000
ufw allow 9000
Below command enables all incoming traffic to ports ranging from 9000 to 9010.
ufw allow 9000:9010/tcp
firewall-cmd
For hosts with firewall-cmd enabled (CentOS), you can use firewall-cmd command to allow traffic to specific ports. Use below commands to allow access to port 9000
firewall-cmd --get-active-zones
This command gets the active zone(s). Now, apply port rules to the relevant zones returned above. For example if the zone is public, use
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=9000/tcp --permanent
Note that permanent makes sure the rules are persistent across firewall start, restart or reload. Finally reload the firewall for changes to take effect.
firewall-cmd --reload
iptables
For hosts with iptables enabled (RHEL, CentOS, etc), you can use iptables command to enable all traffic coming to specific ports. Use below command to allow
access to port 9000
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 9000 -j ACCEPT
service iptables restart
Below command enables all incoming traffic to ports ranging from 9000 to 9010.
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 9000:9010 -j ACCEPT
service iptables restart
Test MinIO Connectivity
Test using MinIO Console
MinIO Server comes with an embedded web based object browser. Point your web browser to http://127.0.0.1:9000 to ensure your server has started successfully.
NOTE: MinIO runs console on random port by default if you wish choose a specific port use
--console-addressto pick a specific interface and port.
Things to consider
MinIO redirects browser access requests to the configured server port (i.e. 127.0.0.1:9000) to the configured Console port. MinIO uses the hostname or IP address specified in the request when building the redirect URL. The URL and port must be accessible by the client for the redirection to work.
For deployments behind a load balancer, proxy, or ingress rule where the MinIO host IP address or port is not public, use the MINIO_BROWSER_REDIRECT_URL environment variable to specify the external hostname for the redirect. The LB/Proxy must have rules for directing traffic to the Console port specifically.
For example, consider a MinIO deployment behind a proxy https://minio.example.net, https://console.minio.example.net with rules for forwarding traffic on port :9000 and :9001 to MinIO and the MinIO Console respectively on the internal network. Set MINIO_BROWSER_REDIRECT_URL to https://console.minio.example.net to ensure the browser receives a valid reachable URL.
Similarly, if your TLS certificates do not have the IP SAN for the MinIO server host, the MinIO Console may fail to validate the connection to the server. Use the MINIO_SERVER_URL environment variable and specify the proxy-accessible hostname of the MinIO server to allow the Console to use the MinIO server API using the TLS certificate.
For example: export MINIO_SERVER_URL="https://minio.example.net"
| Dashboard | Creating a bucket |
|---|---|
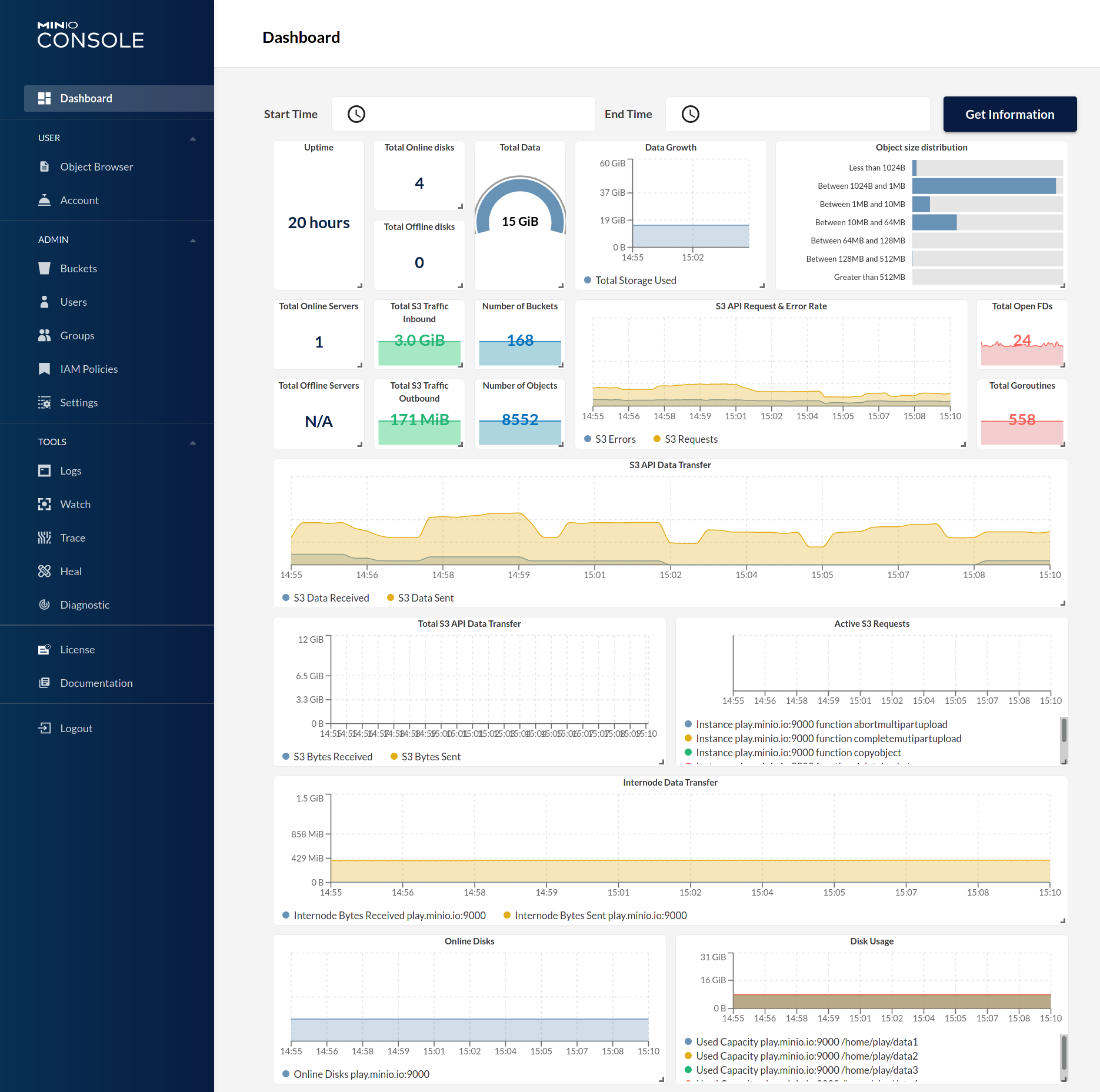 |
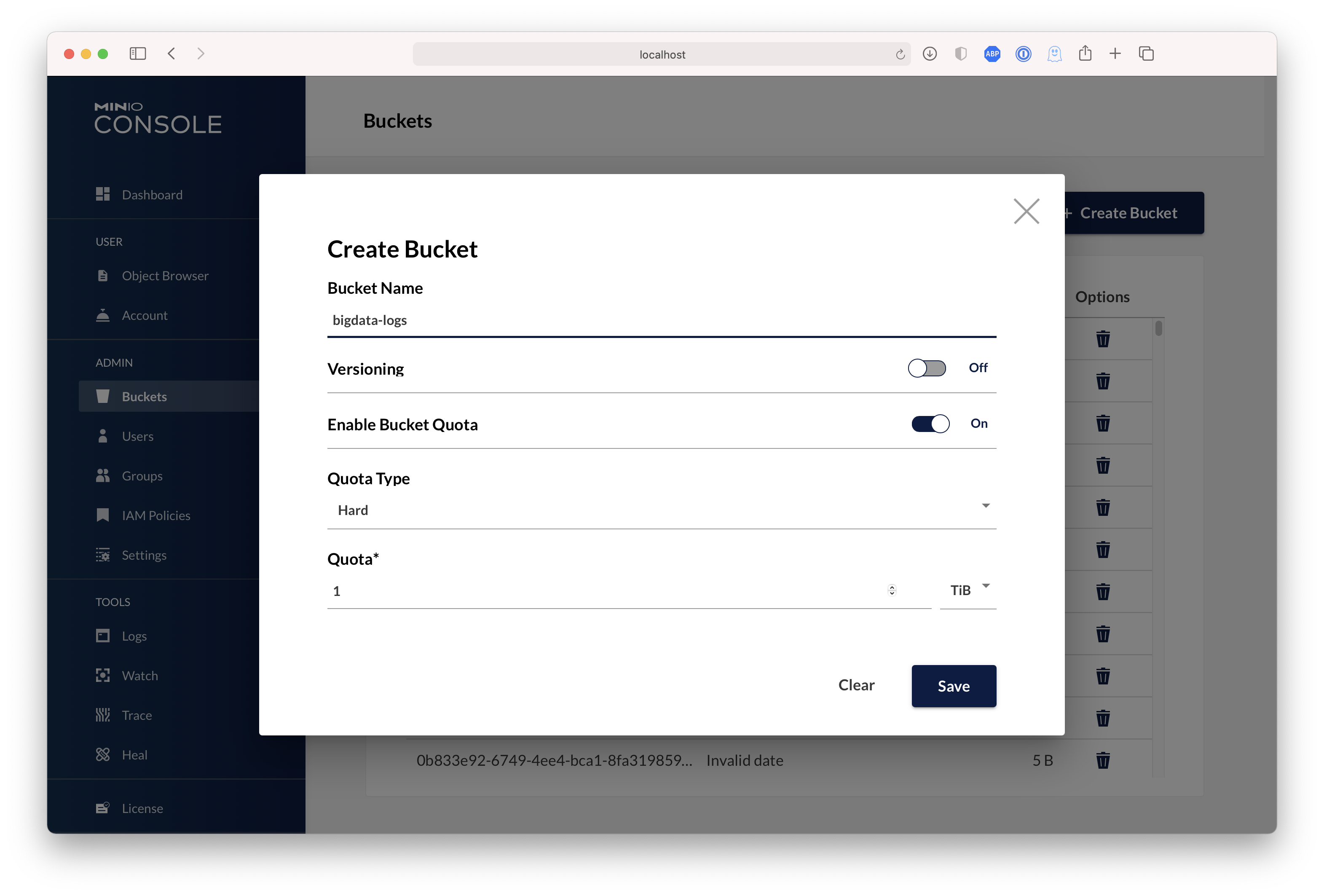 |
Test using MinIO Client mc
mc provides a modern alternative to UNIX commands like ls, cat, cp, mirror, diff etc. It supports filesystems and Amazon S3 compatible cloud storage services. Follow the MinIO Client Quickstart Guide for further instructions.
Explore Further
- MinIO Erasure Code Overview
- Use
mcwith MinIO Server - Use
minio-goSDK with MinIO Server - The MinIO documentation website
Contribute to MinIO Project
Please follow MinIO Contributor's Guide
License
- MinIO source is licensed under the GNU AGPLv3 license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
- MinIO Documentation © 2021 by MinIO, Inc is licensed under CC BY 4.0.
- License Compliance